Packet
Packet
- An IP Packet is the data unit sent at the Network layer.
An IPv4 packet header, depending on the options selected, can range in size from 160 bits (20 bytes) and 480 bits (60 bytes)
- Version
- 4 bits
- Always set to 4 (0100)
- IHL (Internet Header Length)
- 4 bits
- Specifies the number 32-bit words
- 5 words end at the destination IP address
- 6 or more mean that there are Options configured
- DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point)
- 6 bits
- Identifies the kind of service the pack contains, and what priority it should receive, and how likely it is to be dropped during network congestion
- ECN (Explicit Congestion Notification)
- 2 bits
- Total Length
- 16 bits
- Identification
- 16 bits
- Flags
- 3 bits
- Fragment Offset
- 13 bits
- Time To Live
- 8 bits
- Used to prevent routing loops
- Indicates hop count, which each router decrementing the value by 1
- Protocol
- 8 bits
- Indicates the IP Protocol, per an assigned IANA protocol number
- List of IP protocol numbers - Wikipedia
- Header Checksum
- 16 bits
- Source IP Address
- 32 bits
- Destination IP Address
- 42 bits
- Options (if IHL is greater than 5)
- Up to 320 bits long

Source: Internet Protocol version 4 - Wikipedia
Metadata
OSI or TCP/IP Layer
CCNA Exam Topic
Contributors
Sources
IPv6 Header
320 bits in total (40 bytes)
- Version: 4 bits
- Always 6 (0110)
- Traffic class: 6+2 bits
- QoS Markings
- Flow Label: 20 bits
- Used to identify specific traffic flow
- Payload length: 16 bits
- Length of the encapsulated Layer 4 segment
- Next Header: 8 bits
- Indicates the encapsulated Layer 4 protocol
- Hop Limit: 8 bits
- Functions like the IPv4 TTL field
- Source Address: 128 bits
- Destination address: 128 bits
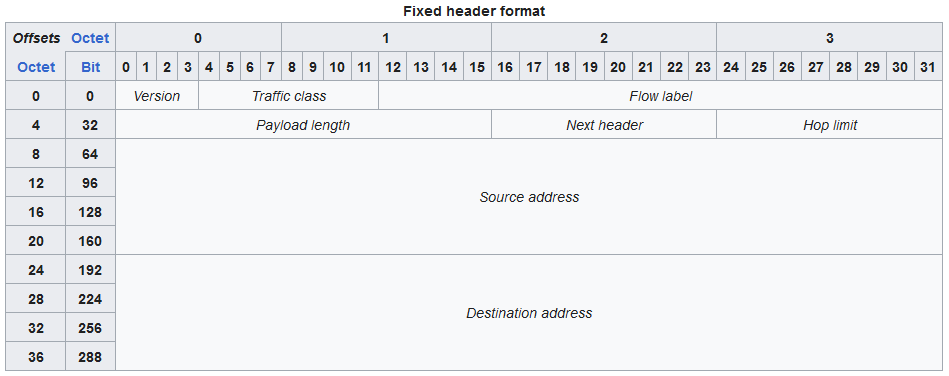
Source: IPv6 packet - Wikipedia
Metadata
OSI or TCP/IP Layer
CCNA Exam Topic
Contributors
Sources
Internet Protocol version 4 - Wikipedia
IPv6 packet - Wikipedia