TCP
TCP
TCP Summary
Transmission Control Protocol is a L4 connection-oriented protocol
- Connection oriented
- Before transmitting data, two hosts establish a connection
- Reliable communication
- Destination host MUST send an acknowledge that it received each TCP Segment
- If a segment isn't acknowledged, it is resent
- Sequencing
- Sequence numbers allow hosts orient segments in the correct order
- Forward Acknowledgement is used to indicate the sequence number of the next segment the host expects to receive
- Provides Flow Control
- Destination can tell source host to change the flow rate of data.
- The TCP header Window Size indicates how many segments can be sent before an ACK is required for them
TCP Header
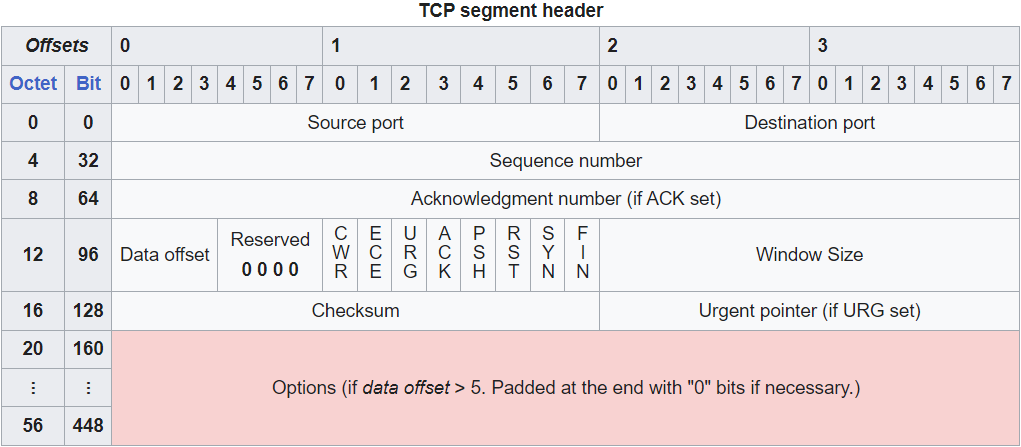
Source: Wikipedia
- The Source and Destination ports are 16 bits long, so there are 65536 available port numbers
- The Sequence number and Acknowledgement number are used to provide sequencing and reliable communication
- There are a series of flags in the 12th octet that are used (when set to 1, they are active)
- Flags used to establish/terminate connections
- ACK
- SYN
- FIN
- Flags used to establish/terminate connections
- Window Size is used for Flow Control
TCP Connection Creation and Termination
TCP Three-Way Handshake (Creation)
- HostA initiates with a Segment with the SYN flag set
- HostB replies with a SYN-ACK flags set
- HostA responds with the ACK bit set
TCP four-way handshake (Termination)
- HostB initiates termination with a FIN flag
- HostA responds with an ACK
- HostA then send it's own segment with a FIN flag
- HostB responds with an ACK
TCP Sequencing
TCP uses Forward Acknowledgement to sequence messages
- Each host tracks its own sequence of messages with the Sequence number
- Each host indicates the next messages sequence number it expects to receive with the Acknowledgement number
- Example of a 3-way handshake and future dataflow:
- HostA starts communication with a SYN segment and a random sequence number of 27
- In practice, the random numbers are much larger and do not increment by 1
- HostB responds with a SYN-ACK segment with a random sequence number of 3, and an acknowledgement number of 28
- The acknowledgement number is in anticipation of receiving a segment with that sequence number
- HostA Responds with an ACK segment with a sequence number of 28, and an acknowledgement number of 4
- HostB responds with segment with a sequence number of 4, and an acknowledgement number of 29
- etc.
- HostA starts communication with a SYN segment and a random sequence number of 27
Common Protocols
Port 21, FTP
Port 22, SSH
Port 23, Telnet
Port 53, DNS
Port 80, HTTP
Port 443, HTTPS