WLC
WLC
Wireless LAN Controller; Used in combination with the CAPWAP (Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points) to manage Lightweight Access Points in large quantities by the network administrator or network operations center.
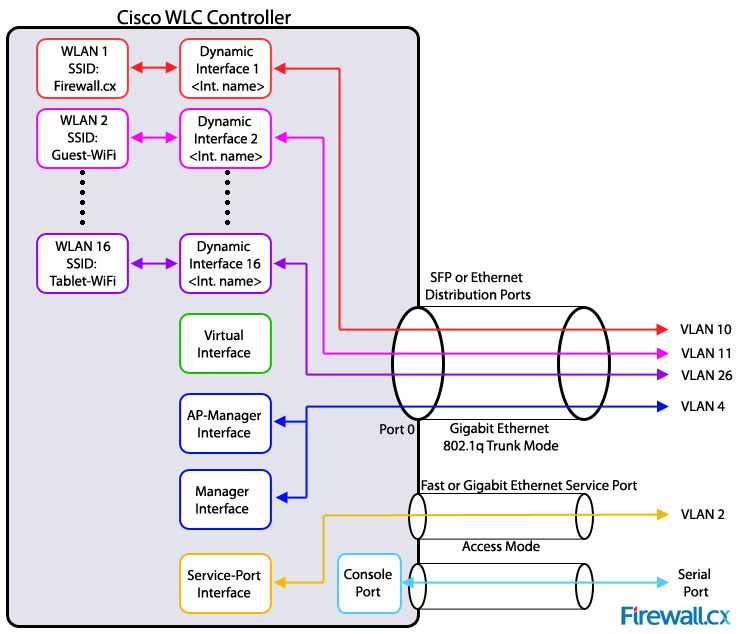
- WLC Ports are physical, and WLC Interfaces are logical (virtual)
WLC Deployment Models
- Four deployment models
- Unified WLC deployment
- The default, WLC is a hardware appliance on the network
- Each WLC can support about 6000 WLCs
- Scale up with more WLCs
- Cloud-based WLC deployment
- (NOT the same as Cloud-based APs)
- WLC is a VM, usually in a private cloud or data center
- Each WLC VM can support 3000 APs
- Scale up with more WLC VMs
- Embedded WLC
- WLC is integrated with a switch
- Each embedded WLC can support up to 200 APs
- Scalable
- Mobility Express WLC
- WLC is integrated with an AP
- Can support up to 100 APs
- Unified WLC deployment
Source: Firewall.cx
WLC Ports
- Service Port
- Used for Out-of-Band (OOB) Management and only supports one LAN
- Must be connected to an access port on the switch
- The Service Port Interface is bound to the Service Port if it's used
- Used for Out-of-Band (OOB) Management and only supports one LAN
- Distribution Port
- Standard network ports that connect to the Distribution System (DS)
- Used for Data Traffic
- Usually connect to switch Trunk ports
- If there's more than one, they all form a LAG by default
- Standard network ports that connect to the Distribution System (DS)
- Console Port
- For direct management; either RJ45 or USB
- Redundancy Port
- Used to physically connect another WLC in an HA Pair
WLC Interfaces
- Management Interface
- Used for management traffic, such as SSH, RADIUS, Syslog, HTTPS, etc.
- CAPWAP tunnels are also formed with this interface
- Redundancy Management Interface
- Used to manage the "standby" WLC in an HA Pair
- Virtual Interface
- Two key roles:
- DHCP Relay (to relay DHCP requests from wireless clients to the DHCP server)
- Redirect address for web authentication (e.g., login page)
- Two key roles:
- Service Port Interface
- Bound to the service port and used for Out-of-Band management
- Dynamic Interfaces
- Map WLANs to VLANs
- e.g., traffic from the "Sales" WLAN is sent to the wired network from the WLC's "Sales" dynamic interface, that's mapped to "VLAN 10 - Sales"
- Map WLANs to VLANs
- AP Manager Interface
- Used for all Layer 3 communications between the WLC and Lightweight APs after they have joined the controller
WLC Management
GUI Orientation
- Monitor Tab
- Overview of information
- Active ports, list of clients and their details, etc.
- Controller Tab
- Create and control interfaces
- Assign netmask, gateway, DHCP server, ACLs, etc.
- When creating Interfaces, you first Name the interface, then assign a VLAN ID
- Create and control interfaces
- WLAN Tab
- Map WLANs to VLANs and configure configure policies for WLANs
- When creating a WLAN, you are asked for the Type, Profile Name, SSID, and ID, in that order
- WLAN Editor Subtab
- General Subtab
- WLANs are created disabled by default; Enable here
- Security Subtab
- Allows you to configure Layer 2 security settings
- Remember: PSK = Personal, 802.1X = Enterprise
- PSK can be either ASCII or Hexadecimal
- Allows you to configure Layer 2 security settings
- QoS Subtab
- Choose the default QoS for that VLAN
- Platinum = Voice
- Gold = Video
- Silver = Best Effort, default
- Bronze = Background
- Choose the default QoS for that VLAN
- Advanced Subtab
- FlexConnect, maximum number of clients, etc.
- General Subtab
- Map WLANs to VLANs and configure configure policies for WLANs
- Wireless Tab
- See and manage all APs connected to the WLC
- Also set AP operational mode
- local
- FlexConnect
- Monitor
- Rogue Detector
- Sniffer
- Bridge
- SE-Connect
- Management Tab
- Security Tab