Diagnostic Commands
There are a variety of Cisco IOS and networking tools you can use for information gather and diagnostics. I've broken them up into a few groups to make them easier to remember, but there will often be overlap.
Connected Device Information
If you want to learn anything about a device, the show command is what you need. There are many sub-commands that you can use to reveal information about the device, but here are a few basic ones you should be familiar with.
show running-config and show startup-config
- Can be used to compare the entire config between devices (or to check for unsaved changes)
- Often a great place to start to gather basic config information.
show interfaces
- Shows detailed Layer 1 and Layer 2 information about all interfaces or a specific interface
- Allows use of the
briefsub-command to summarize information
show ip interface
- Shows detailed Layer 3 information about all interfaces or a specific interface
- Can be summarized with the
briefcommand - Can return IPv6 information with
show ipv6 interface
show ip route
- Shows the Routing Table, which detailed network routes and how they were learned
show cdp neighbors and show lldp neighbors
- CDP is enabled by default on Cisco devices, and communicates identifying information between devices
- This can be very helpful if you don't know which interface a Switch is plugged into, and can help you reconstruct the network topology
show ip protocols
- Shows the running Dynamic Routing Protocols on a device, and their configurations
show arp
- Shows the ARP entry (i.e., IP address and MAC Address) for all interfaces
Network Connectivity
Ping
ping [destination IP]sends ICMP echo requests to a destination IP address- A quick way to test two-way Layer 3 connectivity between hosts
- The ICMP echo request must be able to reach the destination, and the ICMP echo reply must be able to return
Traceroute
- A step further than Ping,
traceroute [destination IP]sends UDP datagrams with incrementing TTL values to a destination IP, with a default target UDP port 33434 - Each hop replies, and the route to the destination IP is mapped out.
Telnet
- While Telnet is not secure for data transmission, it can be used to test Layer 4 connectivity between devices and verify open ports with just
telnet [host name or IP] [port number]- Requires almost no setup, and the receiving device doesn't need to support it
- You will receive a message stating whether the message was successful or nor
Debug and Logging Information
`debug [opt]``
- The debug command shows real-time logging information directly in the console
undebug [opt]andundebug all(or shortened tou all) can stem the flow of information
Host Network Information
Below are sample output commands for the ping and ipconfig/ifconfig for different host operating systems.
Where applicable, I changed the code syntax highlighter to make the output more readable. Nothing really helped with ifconfig.
Ping Command:
-
Windows:
- Command: Open Command Prompt and use the "ping" command.
- Example:
ping google.com - Output:
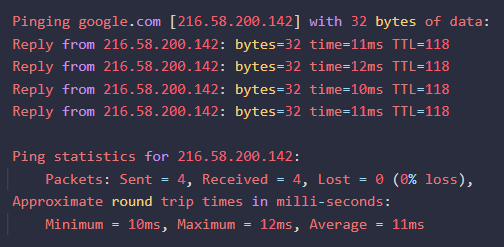
-
Linux (using Terminal):
- Command: Open the terminal and use the "ping" command.
- Example:
ping google.com - Output:
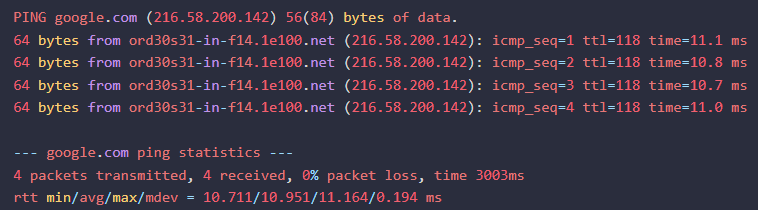
-
macOS (using Terminal):
- Command: Open the terminal and use the "ping" command.
- Example:
ping google.com - Output:
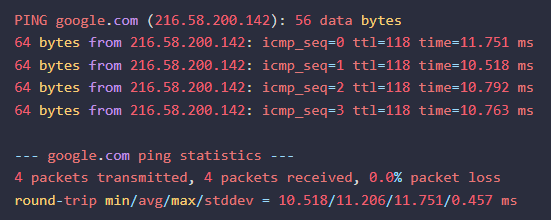
ipconfig/ifconfig Command:
-
Windows:
- Command: Open Command Prompt and use the
ipconfigcommand. - Example:
ipconfig - Output:
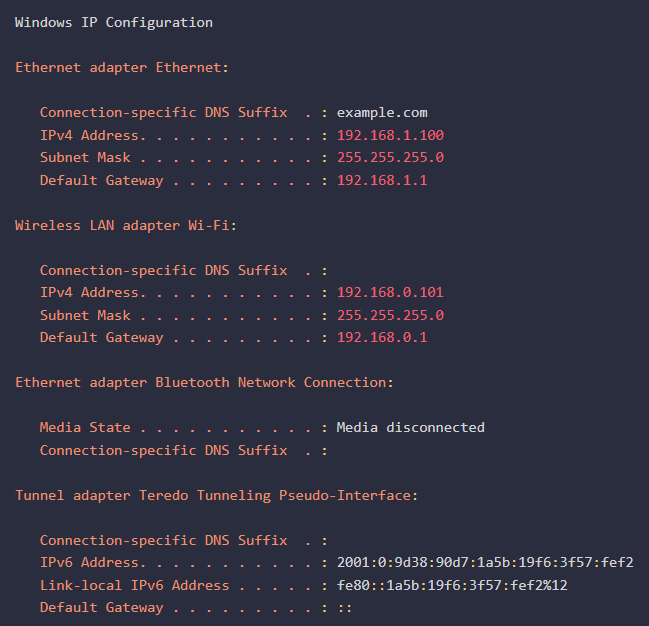
- Command: Open Command Prompt and use the
-
Linux (using Terminal):
- Command: Open the terminal and use the "ifconfig" command.
- Example:
ifconfig - Output:
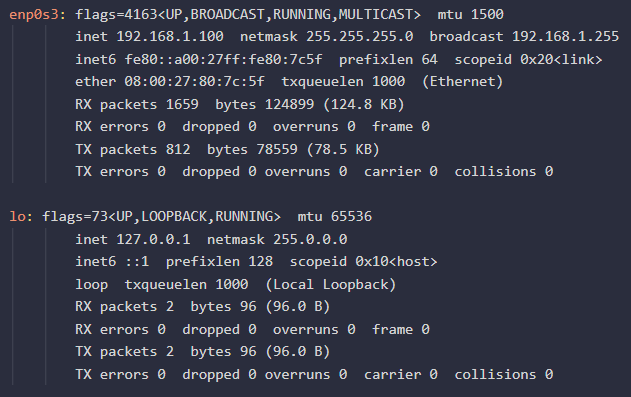
-
macOS (using Terminal):
- Command: Open the terminal and use the "ifconfig" command.
- Example:
ifconfig - Output:
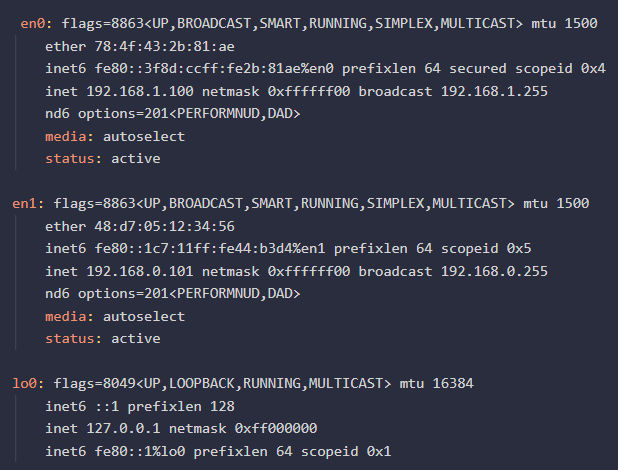
Metadata
OSI or TCP/IP Layer
CCNA Exam Topic
Contributors
Sources
GitHub - HerrSpace/CCNA-Cheat-Sheet: A comprehensive CCNA CLI reference.
Cisco Network Troubleshooting for Beginners | Pluralsight
ping (networking utility) - Wikipedia
traceroute - Wikipedia
Cisco IOS Debug Command Reference